NFT Identity Privacy Comparison Tool
This tool helps you understand the privacy implications of different NFT-based digital identity approaches. Select your preferred approach below to see how it compares to traditional systems.
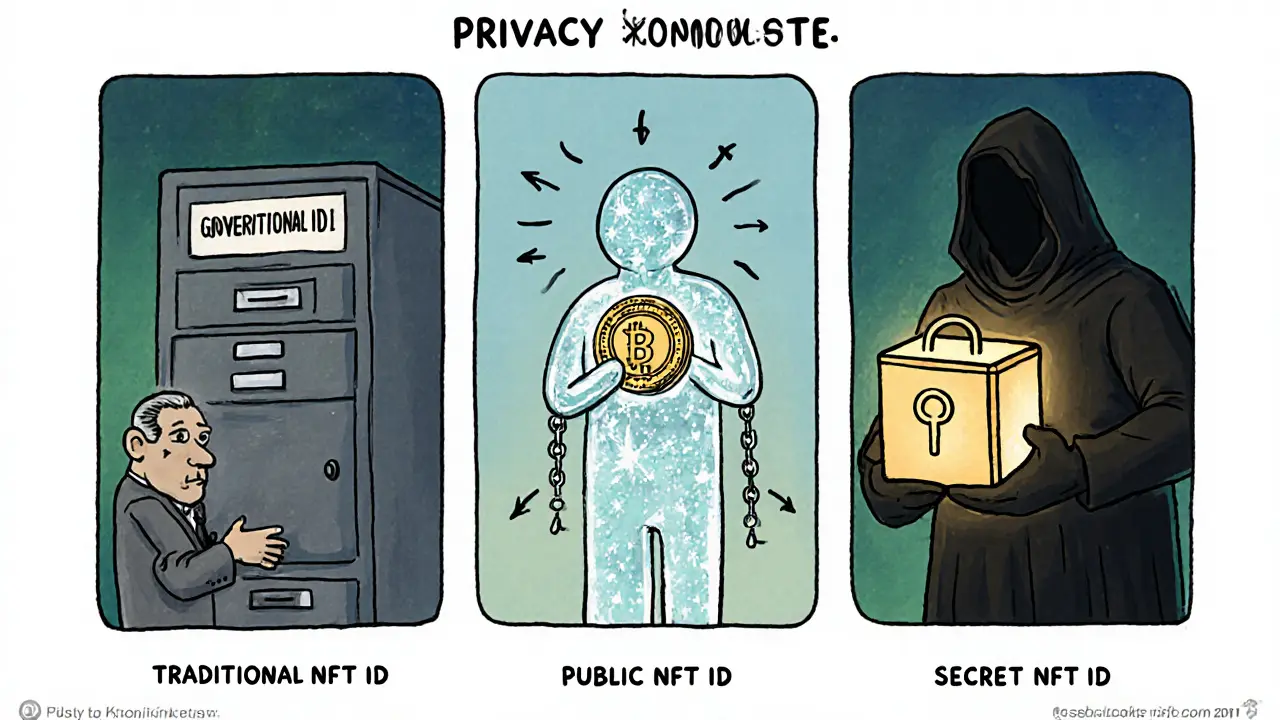
Traditional ID
Centralized databases with limited user control.
Low PrivacyPublic NFT ID
Transparent blockchain storage with full visibility.
High ExposureSecret NFT ID
Encrypted metadata with selective disclosure.
High PrivacyPrivacy Comparison Table
| Aspect | Traditional | Public NFT | Secret NFT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Central servers (prone to breach) | On-chain (transparent) | Encrypted on-chain + private off-chain |
| User Control | Limited, provider-driven | High - wallet holder decides | High - plus optional consent flags |
| Regulatory Compliance | Built-in GDPR/CCPA hooks | Hard to delete data → compliance risk | Supports selective erasure via off-chain |
| Verification Speed | Instant (central query) | Depends on chain latency | Similar to public but extra decryption step |
| Scalability | High (central resources) | Limited by gas and block size | Improved via layer-2 or private nets |
Key Privacy Features
Public NFT Features
- Full blockchain transparency
- Immutable verification
- Easy to audit
- High exposure risk
Secret NFT Features
- Encrypted metadata
- Selective disclosure
- Zero-knowledge proofs
- User-controlled access
Privacy Best Practices
When implementing NFT-based identity solutions:
- Choose privacy-oriented blockchains or layer-2 solutions
- Encrypt all personally identifiable metadata before minting
- Implement zero-knowledge proof flows for attribute verification
- Use non-transferable SBTs for credentials that shouldn't be sold
- Provide clear consent UI so users can audit what they share
Ever wondered how you could prove who you are online without handing over a mountain of personal data to a centralized service? NFT‑based digital identity is a fresh take on that idea, marrying the ownership model of non‑fungible tokens with the need for secure, verifiable credentials. The catch? Blockchains love transparency, and privacy‑focused users hate being traced. This article untangles the knot, walks through the biggest privacy roadblocks, and shows where the industry is heading to keep your personal data under lock and key.
How NFT‑Based Digital Identity Works
At its core, an NFT digital identity is a token‑ized representation of a person’s credentials-think a driver’s license, university degree, or membership card-minted on a blockchain. The token lives in a crypto wallet, and a smart contract (the programmable logic on the chain) dictates what data can be read, who can verify it, and under what conditions it can be shared.
Unlike traditional usernames and passwords, the identity token is cryptographically signed. When a platform asks, “Can you prove you’re over 18?” the wallet can generate a signed proof without revealing the full birthdate. This selective disclosure is possible thanks to advanced cryptographic primitives, most notably zero‑knowledge proofs. The proof confirms the claim while keeping the underlying data hidden.
Core Privacy Challenges
The biggest elephant in the room is that most blockchains are public. Every transaction, every token transfer, every wallet address is visible to anyone with a block explorer. When an NFT holds identity data-whether in the token’s metadata or linked off‑chain-those details can be scraped, indexed, and correlated.
- Transparency vs. confidentiality: Public ledgers give auditors confidence but also let bad actors trace your activity.
- Immutability clash with data‑subject rights: Regulations like the GDPR grant individuals the right to be forgotten, yet a blockchain record can’t be erased.
- Linkability risk: If the same wallet is used across services, a simple address lookup can build a full profile of your online life.
These issues have led experts to label NFTs as great for “what you own” but shaky for “who you are.” The tension is real, and solving it requires more than just clever coding.
Privacy‑Enhancing Solutions
Enter the new generation of privacy‑first tokens. The most talked‑about are Secret NFTs, which hide both ownership and metadata from public view. They achieve this by encrypting the token’s data on‑chain and only decrypting it in the holder’s private environment.
Besides Secret NFTs, several other tools are gaining traction:
- Soulbound Tokens (SBTs): These are non‑transferable NFTs that act as a permanent credential linked to a single address. Because they can’t be sold, they reduce the risk of credential dumping. However, without proper consent mechanisms, anyone could spam an address with unwanted SBTs, raising privacy concerns.
- Zero‑knowledge proof integration: Protocols like zk‑SNARKs let a holder prove attributes (age, citizenship) without exposing raw data.
- Hybrid on‑chain/off‑chain models: Core hashes stay on the public ledger for integrity, while sensitive details live in encrypted off‑chain storage.
- Private blockchain networks: Networks such as Secret Network run consensus in a confidential manner, making every transaction private by default.
All these approaches share a common goal: keep the verification benefit of blockchain while shielding the personal data underneath.
User‑Control Mechanisms
One of the biggest advantages of NFT identity over legacy systems is user sovereignty. With a decentralized wallet, you decide exactly what to share and with whom. Consent can be built directly into the smart contract: a request for a proof will only be fulfilled if the holder signs a transaction approving that specific data slice.
Imagine a concert ticket that’s an NFT. When you walk up to the gate, the venue’s scanner sends a challenge; your wallet replies with a proof that the ticket is valid, but it never discloses your name or other personal details. After the event, the proof expires, leaving no trail.
These user‑centric designs also help mitigate the data‑breach nightmare that plagues Web2 identity providers, where a single breach can expose millions of records at once.
Implementation Hurdles
Turning the privacy promise into a production‑ready system isn’t a walk in the park. Here are the most common pain points developers hit:
- Standardization: Different blockchains use ERC‑721, ERC‑1155, or bespoke standards. Interoperability layers are still early‑stage.
- Scalability: Verifying zero‑knowledge proofs can be computationally heavy, especially on public chains with high gas fees.
- User education: Many end‑users still think of NFTs as art collectibles, not as secure credentials. Clear UI/UX is essential.
- Regulatory uncertainty: Jurisdictions differ on how digital identity tokens fit within existing data‑protection frameworks.
Addressing these hurdles often means blending on‑chain verification with off‑chain privacy layers, and staying agile as regulators update guidance.
Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Centralized ID | Public NFT‑Based ID | Secret NFT‑Based ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data storage | Central servers (prone to breach) | On‑chain (transparent) | Encrypted on‑chain + private off‑chain |
| User control | Limited, provider‑driven | High - wallet holder decides | High - plus optional consent flags |
| Regulatory compliance | Built‑in GDPR/CCPA hooks | Hard to delete data → compliance risk | Supports selective erasure via off‑chain |
| Verification speed | Instant (central query) | Depends on chain latency | Similar to public but extra decryption step |
| Scalability | High (central resources) | Limited by gas and block size | Improved via layer‑2 or private nets |
Notice how Secret NFTs flip many of the privacy downsides of a plain public token while keeping the verification benefits. They’re not a silver bullet, but they’re the closest we have right now.
Best‑Practice Checklist for Privacy‑First NFT Identity
- Choose a privacy‑oriented blockchain or layer‑2 solution.
- Encrypt all personally identifiable metadata before minting.
- Implement zero‑knowledge proof flows for attribute verification.
- Use non‑transferable SBTs for credentials that shouldn’t be sold.
- Provide a clear consent UI so users can audit what they share.
- Plan for GDPR‑style requests: store raw data off‑chain where it can be deleted.
- Stay updated on regulatory guidance for digital identity in your jurisdiction.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a regular NFT to store my passport data?
Technically you can, but a regular NFT lives on a public chain, so anyone can read the metadata. That violates most data‑protection laws and defeats the purpose of privacy.
What’s the difference between a Secret NFT and a regular NFT?
A Secret NFT encrypts its metadata and ownership details, only decryptable by the holder’s private key. A regular NFT’s data is fully visible to anyone browsing the blockchain.
Do zero‑knowledge proofs expose any of my personal info?
No. Zero‑knowledge proofs let you prove a statement (e.g., “I am over 21”) without revealing the underlying data (your exact birthdate).
Are soulbound tokens safe from spam?
Only if the contract includes consent checks. Without them, anyone could issue unwanted SBTs to an address, creating privacy noise.
How do regulators view NFT‑based identity?
Regulators are still forming guidelines. The main concerns are data immutability vs. the right to be forgotten, and the potential for unauthorized profiling.
Privacy in NFT‑based digital identity isn’t a solved problem, but the toolbox is growing. By picking the right blockchain, encrypting metadata, and leveraging zero‑knowledge proofs, you can get the best of both worlds: a tamper‑proof credential that stays under your control. Stay curious, stay secure, and watch the standards evolve-your digital self depends on it.


mark gray
April 6, 2025 AT 04:45I think the comparison table does a solid job of highlighting where secret NFTs shine, especially around user control and data erasure.
Alie Thompson
April 7, 2025 AT 22:25It's frankly alarming how many developers rush to mint public NFTs for identity without even considering the basic ethical implications. The very premise of exposing personally identifiable information on an immutable ledger contradicts the spirit of data protection laws. Moreover, the casual attitude toward GDPR compliance shows a dangerous disregard for individual rights. When you implement a public NFT ID, you essentially hand over a permanent, searchable fingerprint to the world. This is not a minor oversight; it is a blatant violation of privacy that can be exploited by malicious actors. The industry must adopt secret NFT solutions as the default, not the exception. Only then can we claim to respect user sovereignty while maintaining regulatory standards.
Samuel Wilson
April 9, 2025 AT 16:05The article presents a comprehensive overview of the privacy landscape surrounding NFT‑based digital identity, and it is valuable to dissect each component methodically. First, the distinction between public and secret NFTs is crucial because it directly influences the exposure risk profile. Public NFTs, by definition, store metadata on a transparent ledger, making any attached personal data instantly visible to any observer with a block explorer. In contrast, secret NFTs encrypt this metadata, limiting readability to the holder's private key, which aligns more closely with GDPR's data minimisation principles. Second, the integration of zero‑knowledge proofs (ZKPs) offers a powerful mechanism for selective disclosure; a holder can prove age or citizenship without revealing the underlying data points. Third, the use of soulbound tokens (SBTs) introduces non‑transferability, reducing the likelihood of credential resale and associated privacy noise, yet they require consent checks to prevent spam. Fourth, the scalability concerns surrounding ZKP verification and gas fees on public chains necessitate layer‑2 solutions or privacy‑oriented blockchains such as Secret Network. Fifth, regulatory compliance remains a moving target; the immutable nature of blockchain records must be reconciled with the right to be forgotten, potentially via off‑chain storage of raw data that can be deleted upon request. Sixth, user‑centric consent mechanisms embedded in smart contracts empower individuals to approve each data request explicitly, thereby limiting inadvertent data leakage. Seventh, the article correctly highlights the importance of clear UI/UX to educate users who may conflate NFTs with digital art rather than credentials. Eighth, the suggested best‑practice checklist underscores essential steps such as encrypting metadata prior to minting and planning for GDPR‑style data erasure. Ninth, the comparative table succinctly illustrates trade‑offs in storage, control, compliance, speed, and scalability, which serves as a handy decision‑making tool for developers. Tenth, adopting hybrid on‑chain/off‑chain models balances transparency with privacy by anchoring hashes on‑chain while keeping sensitive details off‑chain. Eleventh, the notion of employing non‑transferable SBTs for non‑sellable credentials adds another layer of protection. Twelfth, the ongoing evolution of standards and regulatory guidance necessitates continuous monitoring by implementers. Thirteenth, community‑driven open standards will be vital for interoperability across different blockchain ecosystems. Fourteenth, the potential for decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to integrate with NFT identity solutions could further enhance privacy guarantees. Fifteenth, future research should explore more efficient ZKP constructions to mitigate computational overhead. Finally, the article makes a compelling case that while privacy challenges are significant, the toolbox of secret NFTs, ZKPs, and consent‑driven smart contracts offers a promising path forward.
Rae Harris
April 11, 2025 AT 09:45Look, the hype train for NFTs often forgets that the blockchain's main feature is transparency, not secrecy, so when you try to stuff personal data into a public token you’re basically handing the world a free telescope to spy on you, which is why the secret NFT approach feels like the only sensible compromise.
Danny Locher
April 13, 2025 AT 03:25Nice breakdown of the pros and cons.
Emily Pelton
April 14, 2025 AT 21:05While the comparison is useful, it’s absolutely critical to remember that without rigorous encryption standards, even “secret” NFTs can be vulnerable to side‑channel attacks; developers must implement hardware‑backed key storage, regularly rotate keys, and conduct third‑party audits, otherwise the whole privacy promise collapses under scrutiny! Moreover, user education is not optional – every wallet UI should clearly display what data is being disclosed at any given moment, and must require explicit consent before any proof is generated. Failure to do so not only erodes trust but also opens the door to massive regulatory penalties.
sandi khardani
April 16, 2025 AT 14:45The whole NFT identity thing is a classic case of tech evangelists ignoring the fundamental security trade‑offs for the sake of buzzwords. They parade zero‑knowledge proofs like a miracle cure, yet they forget that the underlying cryptographic primitives can have subtle vulnerabilities that only surface after years of real‑world usage. On top of that, the ecosystems around secret NFTs are still in their infancy, meaning tooling is scarce, developer expertise is limited, and the threat surface is largely uncharted. If you’re looking to deploy a production‑grade identity system, you should be skeptical of any solution that promises easy integration without a deep audit trail. In short, the hype far outpaces the hard security realities.
Donald Barrett
April 18, 2025 AT 08:25Exactly, and the fact that many projects skip proper key management only makes it worse – a single compromised wallet can expose the whole identity network.
Christina Norberto
April 20, 2025 AT 02:05From a regulatory standpoint, the irrevocability of blockchain records remains a profound obstacle to compliance with the EU's right‑to‑be‑forgotten provisions; until a robust on‑chain erasure mechanism is standardized, secret NFT implementations will continue to operate in a legal gray area, exposing issuers to potential enforcement actions.
Fiona Chow
April 21, 2025 AT 19:45Oh sure, because what the world really needs is another legal nightmare wrapped in cryptic code, right?
Rebecca Stowe
April 23, 2025 AT 13:25Finding the right balance between privacy and usability will be key, and I’m hopeful the community can get there.
Kailey Shelton
April 25, 2025 AT 07:05Meh, seems like another tech fad to me.
Angela Yeager
April 27, 2025 AT 00:45Actually, the detailed checklist is quite helpful for teams beginning their journey; especially the point about off‑chain storage for raw data to satisfy deletion requests.
vipin kumar
April 28, 2025 AT 18:25Don’t forget that the major players are already planning back‑doors into these systems under the guise of “national security” – that’s why we need truly decentralized, privacy‑first protocols now.
Vaishnavi Singh
April 30, 2025 AT 12:05One might argue that the philosophical underpinnings of self‑sovereign identity echo ancient concepts of personal autonomy, yet the digital instantiation through NFTs raises novel epistemological questions about the nature of proof and trust.
Kevin Fellows
May 2, 2025 AT 05:45Cool stuff! Can’t wait to see more projects try out secret NFTs.
victor white
May 3, 2025 AT 23:25While the mainstream narrative glorifies transparency, the cultivated oblivion of the masses serves the interests of entrenched powers; secret NFTs, though framed as empowerment, may simply redistribute surveillance capabilities under a veneer of consent.
Lara Cocchetti
May 5, 2025 AT 17:05It’s disheartening to see such techno‑idealism ignore the very real potential for abuse; moral clarity demands stricter oversight.
Mark Briggs
May 7, 2025 AT 10:45All this hype is just smoke; the code’s not ready.
Millsaps Delaine
May 9, 2025 AT 04:25Honestly, the discourse is saturated with buzzwords while ignoring the lived experience of users who will bear the brunt of any privacy breach.
Anthony R
May 10, 2025 AT 22:05It is noteworthy, however, that the comparative matrix provides a concise visual aid; it could be further enhanced by incorporating risk scores for each privacy dimension.
Cody Harrington
May 12, 2025 AT 15:45Thanks for the thorough breakdown; looking forward to collaborating on future improvements.